Preterm babies are newborn babies who are born before the completion of the pregnancy period, that is thirty-seven weeks of pregnancy. Preterm babies can be segregated into late preterm (born between 34-36 months), moderately preterm (born between 32-34 weeks), very preterm (born between 28-32 weeks) and extreme preterm (born before 28 weeks). Preterm baby care in the NICU hospital is essential for the health of premature infants.
Why is Premature Baby Care Essential?

Premature baby care in hospitals is essential because the preemies are not fully developed to deal with life. There are high instances of preterm birth in American hospitals. The mortality rate among premature babies is high because they have underdeveloped organs like lungs, digestive system and immune system. Today, medical treatment is advanced enough to provide intensive care to infants in their gestation period.
Your premature baby will need the special care of baby specialists. Preterm babies might suffer from respiratory distress syndrome or bronchopulmonary dysplasia. The infant might suffer from jaundice, anaemia of prematurity, temporary pauses in breathing known as apnea and other infections. Some infants also develop a problem in the retina from prematurity. Therefore once your preterm baby is shifted to the NICU after birth, several tests are conducted to ward off chances of complications.
Care at the Hospital
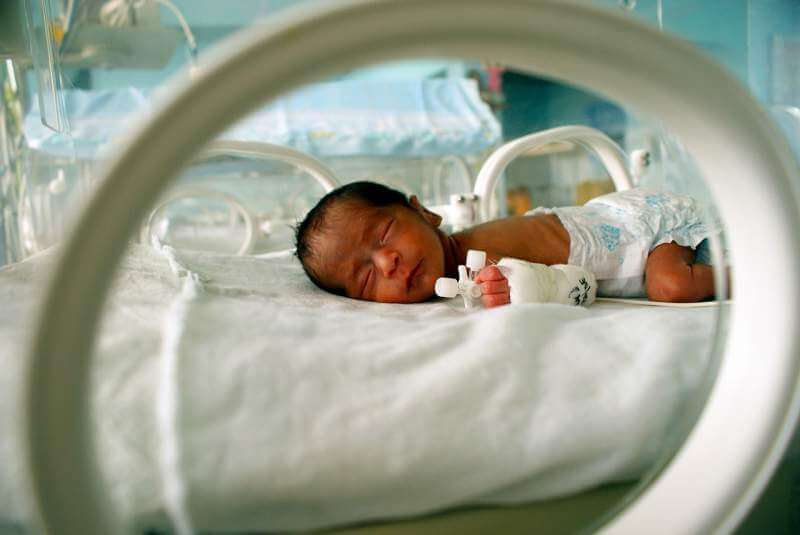
- Tests: Your baby specialist will constantly monitor the baby’s breathing and heart rate. The point is, an early assessment will help prevent deaths. A diligent NICU team will keep a check on the baby’s fluid input and output. Blood tests will be conducted at the hospital to check calcium, glucose and bilirubin levels. An echocardiogram may also be conducted to check the condition of the heart at birth. All of this is to ensure the well-being of your baby and not to scare the parents. The new century doctors may even conduct an ultrasound and eye exam to avoid complications at large.
- Incubator: An incubator is an enclosed plastic bassinet where your preterm baby will be kept in the gestation period. An incubator helps your baby maintain his/her normal body temperature. The nurses will also teach you to keep your baby in direct skin contact with you which is known as “kangaroo” care. This helps the baby stay warm.
- Monitoring of vital signs: Your baby will be monitored closely at the intensive care unit for blood pressure, breathing, heart rate and body temperature. Your baby specialist might also provide a ventilator to help premature infants breathe properly.
- Using a feeding tube: After birth, a preterm baby is given fluids and nutrients through intravenous tubes. Later breastmilk is given through a tube either passing through your baby’s nose or stomach. Breastfeeding or bottle-feeding is possible only when the baby is stable enough to suck.
- Replenishing fluids: A nurse will closely monitor your baby’s fluids, sodium and potassium levels to replenish if anything is deficient. If any fluids are deficient, the doctors will replenish them by providing IV (intravenous) solutions.
- Providing blue light therapy: Many preterm children suffer from jaundice. To increase chances of survival, they are placed under a set of lights known as bilirubin lights. A preterm baby’s liver cannot function properly thereby increasing his/her bilirubin. The blue lights treat this problem by breaking down bilirubin buildup. Your baby will be given a protective eye mask for comfort.
- Blood transfusion: A preterm baby might suffer from anaemia because of several blood tests. Therefore, to prevent any blood-related disease, doctors might suggest a blood transfusion to increase blood volumes.
Medicines given to preterm babies
Your baby specialist will prescribe medicines to your preterm baby to ensure normal functioning of the heart, lungs and brain. Many life-saving drugs are given at the time of birth to ensure the survival of the baby.
- Aerosolized or IV medicines are used to strengthen heart rate and breathing.
- Antibiotics are given to reduce the risk of any infections.
- Medicines known as diuretics are given to maintain fluid balance.
- An injection is given to reduce the chances of retinopathy of prematurity.
- A medicine called surfactant is given to treat respiratory disease syndrome.
- If a preterm baby shows symptoms of a heart disease called patent ductus arteriosus, medicines are given to treat the heart defect.
Surgery
Sometimes the baby specialist might suggest surgery to cure certain birth defects. You as parents will be informed about every procedure if you come to that stage. Your doctors will leave no stone unturned to save the life of your precious.
Care at home

Once you bring the baby home Preterm baby care is as essential at home as it was in the hospital. As new parents, you may be worried about how well you can take care of your baby without the doctor guiding you at every step. Your preemies are ready to go home only when they can breathe properly outside the incubator without any support. Your doctor will discharge your baby only when he/she is ready to bottle feed or breastfeed. Your baby specialist will also make sure that the baby is free from all infections.
Before discharging a preterm baby from the hospital, your doctors and nursing team will make sure that you know all the methods of baby care. Your doctor will suggest that you keep the premature baby away from crowded places.
Premature babies are at high risk of contracting infections, therefore one must be very careful while caring for them. You should be in regular touch with your baby specialist. Every developmental progress of the child must be monitored.
Parenthood is a beautiful experience. Enjoy the experience while taking good care of your newborn.
Reference:
- https://www.who.int/news-room/q-a-detail/newborn-health-caring-for-preterm-babies
- https://www.healthychildren.org/English/ages-stages/baby/preemie/Pages/Caring-For-A-Premature-Baby.aspx
- https://reproductive-health-journal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1742-4755-10-S1-S5
- https://kidshealth.org/en/parents/preemie-home.html
