Kidney stone is a common urinary tract disorder and it is medically coined as urolithiasis. This disorder affects nearly one tenth population of India. It can easily be cured through medications and surgery.
What exactly is kidney stone?
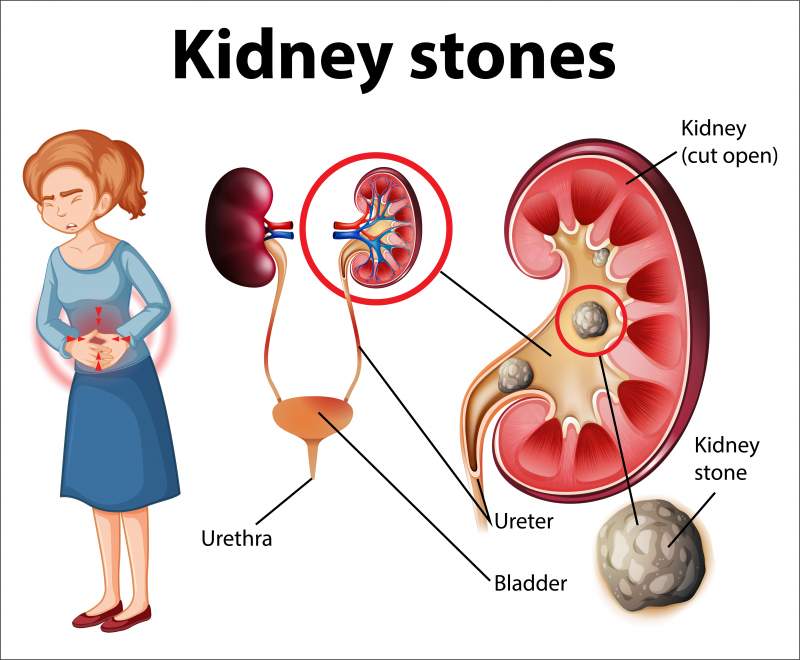
Kidneys resemble shape of beans and are located in upper abdominal cavity. The primary function of kidneys is to filter out or extract waste materials from blood and create urine. They also help in balancing body fluids. To produce one or two quarts of urine, kidneys have to process approximately two hundred quarts of blood.
Urinary tract comprises of two kidneys, two ureters, a urethra and a bladder. Urine is carried from both the kidneys to bladder through tube like structures called ureters. Urine is stored in the bladder and finally passed out of the body through another tube called as urethra.
Sometimes, salts and minerals (generally a combination of calcium oxalate and uric acid) in the urine, stick to each other forming a small stone like structure called kidney stone. These stones are formed in the kidney and pass through urinary track. Size of stones may vary from 2 millimeters to 5 millimeters. Small sized stones pass through urine without causing any discomfort. But, when size of the stone outgrows 5 millimeters, it may block ureter leading to severe lower back or abdominal pain.
What are the types of kidney stones?
There are four major types of kidney stones:
- Calcium stones: Calcium stones are common types of kidney stones and occur in two categories- calcium oxalate and calcium phosphate. Calcium oxalate stones are formed when there is excess calcium oxalate intake via different medications or by drinking high amount of hard water. Calcium phosphate stones are formed when urine has high pH value, i.e., combination of calcium molecules in urine and alkaline urine.
- Uric acid stones: When concentration of uric acid in urine increases, it forms stones by itself or by combining with calcium. Persistent acidic urine can also cause uric acid stones. Consuming diet rich in meats, fish can cause uric acid stones as they contain a substance called purine. Purine facilitates formation of acidic urine.
- Struvite stones : Struvite stones are formed because of kidney or urinary tract infection.
- Cystine stones: It is a genetic type of kidney stone. When cystine from the kidney leaks into the urine, it results in formation of crystals and thereby stones.
What are the symptoms of kidney stone?
Small stones pass easily through urine and show no symptoms as such. Only when the size of stone is moderate, symptoms of kidney stone can be interpreted. Some symptoms of kidney stone are enlisted here:
- Experiencing pain while urinating
- Blood in urine medically termed as hematuria
- Severe pain in lower abdomen or lower back
- Vomiting
- Nausea
- Restlessness
- Sweating
- Fever
- Urge to urinate more often than usual
What causes kidney stone?
- Consumption of certain foods may promote chance of developing kidney stone in people who are susceptible to it, but there is no evidence that eating certain foods will cause kidney stone development in people who are not susceptible
- Kidney stone disorder can be hereditary. If one of your parents has kidney stone disorder, it might be passed down to you as well.
- In cystic kidney diseases, fluid sacs form on kidneys and may cause kidney stone
- Not drinking enough fluids (dehydration) is a major cause of kidney stone
- Cystinuria (high levels of amino acid cystine in urine)
- Hyperoxaluria (large amounts of oxalate crystals in urine)
- Hyperuricosuria (uric acid metabolism disorder)
- Gastrointestinal tract surgery may also cause kidney stone
- Bowel chronic inflammation
- Antacids containing calcium
- Blockage in urinary tract
How are kidney stones diagnosed?
To diagnose kidney stones, various tests such as blood test, urine test, imaging test etc. may be performed. You may also be asked to give details about family history of kidney stone, gastrointestinal problems, diet and other diseases.
- Urinalysis: Urine sample is collected in a special container and is analyzed to detect urine infection or presence of substance that can cause kidney stone.
- Abdominal X-ray: Abdominal X-ray is reviewed by radiologist (person who specializes in medical imaging) to detect the presence and location of kidney stones. Sometimes, more than one X-ray image is required for accurate interpretation of size and location of kidney stone.
- Blood test: Tiny amount of blood is drawn from patient’s body and is analyzed to determine presence of biochemical substances that can cause kidney stones.
- CT Scans: Computed Tomography Scan (CT Scan) makes use of three dimensional images (3D images) to show precise location and size of kidney stone. Patient is required to lie down on a table that slides down into a tunnel where X-ray images are taken.
Treatment of kidney stones
Treatment of kidney stones counts upon various factors such as size of kidney stone and its location. It can be treated by an urologist (a person who specializes in urine related disorders) or general practitioner.
- Ureteroscopy: In this procedure, patient is administered general anesthesia and can go home on the same day of surgery. Ureteroscope, which is a type of endoscope- a long, thin, optical tube-like device that is used to examine underlying, deep parts of body, is used during this procedure. Either of flexible or rigid fiber can be used depending upon the condition.
Ureteroscope is inserted into urethra (thin tube through which urine is passed) and then slided down to bladder (part where urine is stored) and further into ureter (tube like structures that connect kidney to bladder). Only the lower part of ureter or two-third part of ureter is accessed in this procedure. Small stones can easily be removed at one go whereas big sized stones are broken down into pieces before removal. The stones are then passed out of the body through urine.
- Shock wave lithotripsy: In this treatment, lithotripter is used. Patient is made to lie down on a table and is subjected to shock waves generated by the instrument. These shock waves break down kidney stones into smaller pieces and can easily be thrown out of body through urinary tract. This procedure is performed by an urologist by administering general anesthesia. Cost of Lithotripsy in major Indian cities can be found here
- Percutaneous nephrolithotomy: An instrument called nephroscope is used to locate and remove kidney stones. A small incision is made on patient’s back and a tube is inserted directly into the kidney via this incision. Small stones are easily removed whereas lithotripter is used to remove large stones. Lithotripter crushes large stones into smaller pieces.
After the surgery, a small tube called nephrostomy tube is inserted into kidney through skin. This tube helps in draining urine and other residual matter from the kidney into urine collection bag. Patient is required to stay in the hospital for few days after the surgery. This surgery is practiced by urologists by administering general anesthesia.
How can kidney stones be prevented?
Diet plays an indispensable role in preventing kidney stone disorders. As the saying goes “precaution is better than cure,” one must alter diet or take precautionary measures to prevent formation of kidney stones.
- Increasing fluid intake in form of fruit juices, lemonade, coconut water etc. will prohibit formation of kidney stones
- One must consume at least 2-3 liters of water daily for proper hydration
- Purine, a substance found in animal sources of protein such as meat and fish, can cause kidney stones. Hence, restrict intake of meat and fish to prevent kidney stone disorders.
- Reduce use of sodium
- Consult with doctor before taking calcium supplements
- Consume foods (spinach, nuts, wheat bran etc.) having large oxalate content in moderation
- Avoid drinking hard water as it can lead to kidney stone formation
Following above mentioned tips will reduce your chances of kidney stone formation.
Kidney stones are not formed overnight. Constant accumulation of calcium oxalate crystals or uric acid over long period of time can lead to kidney stones. Hence, it is advised to take proper care of diet so as to prevent kidney stone formation.
